Introduction to the IoT: key concepts and key use cases
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming our daily lives by connecting the physical and digital worlds. Behind this acronym lies a technological revolution that is redefining the way we interact with our environment. Let’s start with an introduction to the IoT: what is it, what are its basic concepts, and how is this technology finding applications in various sectors? This article provides an overview.
What is IoT?
The IoT brings together a range of physical objects connected to the Internet, capable of collecting, transmitting and, in some cases, analysing data in real time. These objects range from domestic appliances such as smart thermostats to sophisticated industrial equipment, agricultural sensors and portable health devices.
Unlike traditional electronics, IoT devices often incorporate artificial intelligence, enabling them to anticipate user needs and act autonomously. In short, the IoT represents a global ‘nervous system’, woven together by inter-object connections, making our world more interactive and responsive.
Key IoT concepts
- Sensors and data collection:
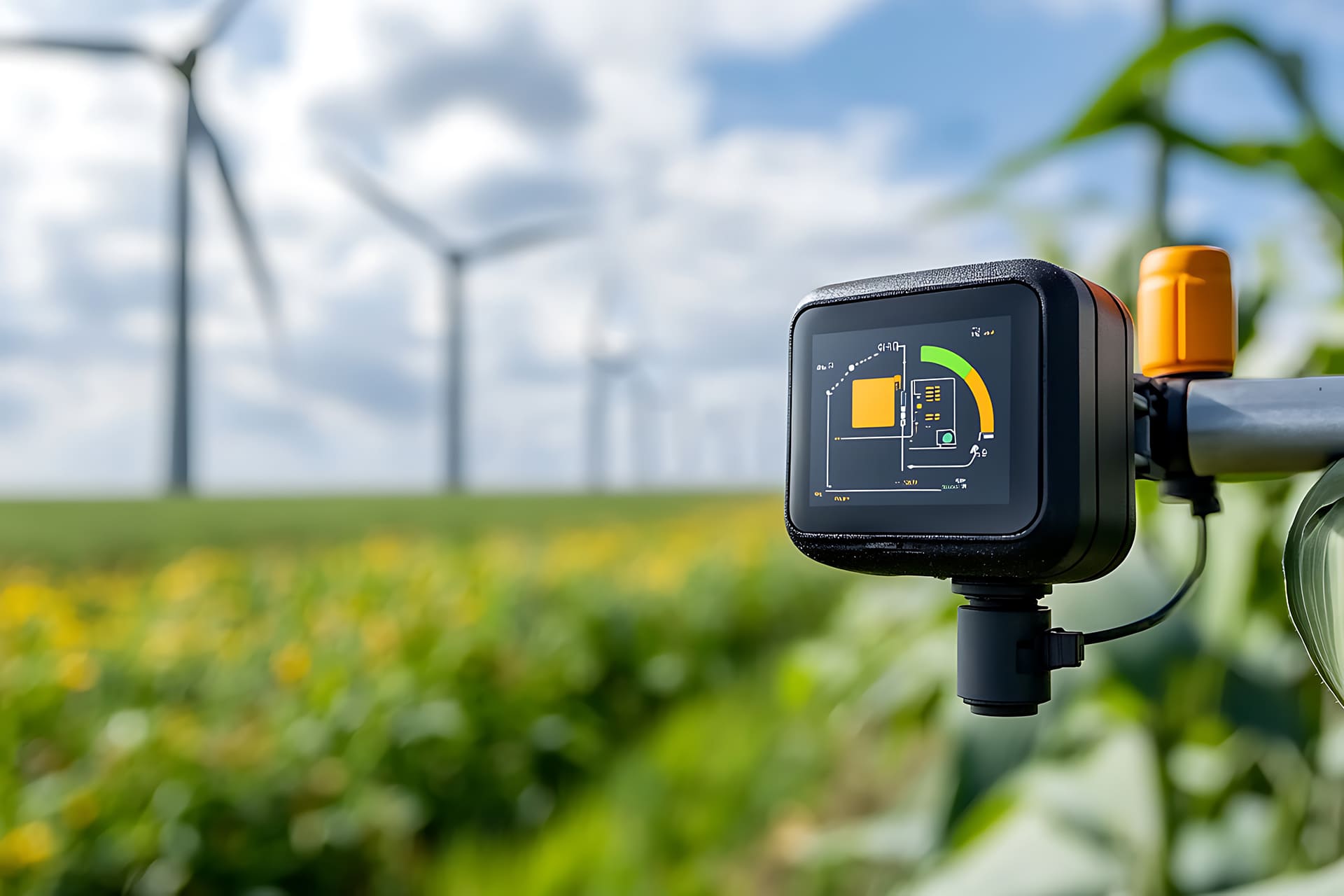
Sensors are the cornerstone of the IoT. They measure variables such as temperature, pressure or movement, converting this data into usable signals. - Connectivity:
To function, IoT objects need to communicate with each other or with management platforms via technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LoRaWAN- or ZigBee-based networks. - Processing and analysis:
The data collected is then stored, often in the cloud, and analysed to generate actionable information, whether for real-time monitoring or future optimisation. - User interface:
IoT platforms allow users to interact with devices, via mobile apps or web interfaces, making objects accessible and easy to control.
Essential use cases
The IoT has applications in almost every sector of the economy. Here are just a few examples:
Home automation:
Smart homes use IoT devices to improve comfort, security and energy efficiency. For example, a connected thermostat automatically adjusts the temperature according to your habits.
Health:
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, can track health parameters in real time, such as heart rate, helping to prevent medical emergencies.
Industry:
Factories are adopting the IoT to optimise their processes, with sensors monitoring machinery in real time and activating predictive maintenance.
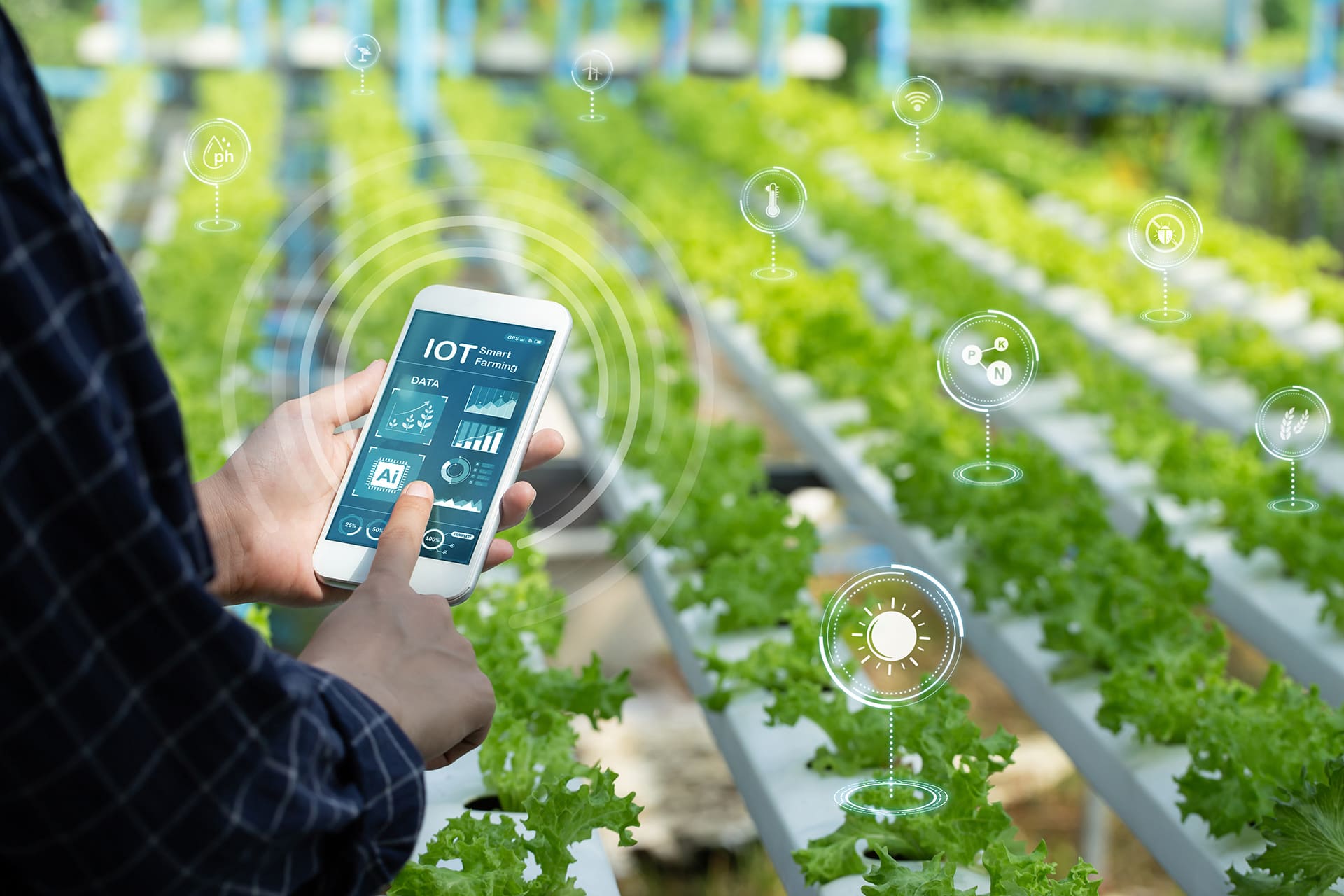
Agriculture:
Thanks to IoT sensors, farmers can monitor soil conditions and adjust irrigation to maximise yields while minimising the resources used.
Transport:
Connected cars and IoT-based traffic management solutions can reduce congestion, improve safety and optimise routes.
The future of the IoT: infinite opportunities
Despite a temporary slowdown in the hype surrounding the IoT, this technology continues to develop, particularly with advances in artificial intelligence and 5G connectivity. These innovations promise to multiply the number of use cases, making the IoT more accessible and powerful than ever.
As we enter an era where every object can become ‘intelligent’, it is essential for businesses to see the IoT not as a fad, but as an essential strategic opportunity.
The IoT is no longer a futuristic vision, but a reality that is shaping our daily lives and our industries.
Whether it’s improving quality of life or optimising industrial operations, this technology offers immense potential. For companies looking to get started, it’s crucial to understand the key concepts and use cases in order to maximise the benefits.
Do you have an IoT project in mind? Start exploring now how this technological revolution can meet your specific needs!